Ethical Considerations
in AI Translation
18
Hey there, friend! Have you ever marveled at how technology can break down language barriers, making the world feel like a smaller, more connected place? Today’s conversation is all about the fascinating world of artificial intelligence (AI) in translation and the important ethical considerations we need to keep in mind. So, grab a cup of coffee, and let’s dive into this together.
The Rapid Evolution of AI in Translation
AI has come a long way since its inception in the mid-20th century. It’s no longer just a sci-fi concept; it’s a reality that’s transforming industries worldwide. One of the most exciting areas of AI application is in translation and localization. AI-driven tools like neural machine translation (NMT) and automatic speech recognition (ASR) have revolutionized the way we communicate globally.
Key Benefits of AI in Translation
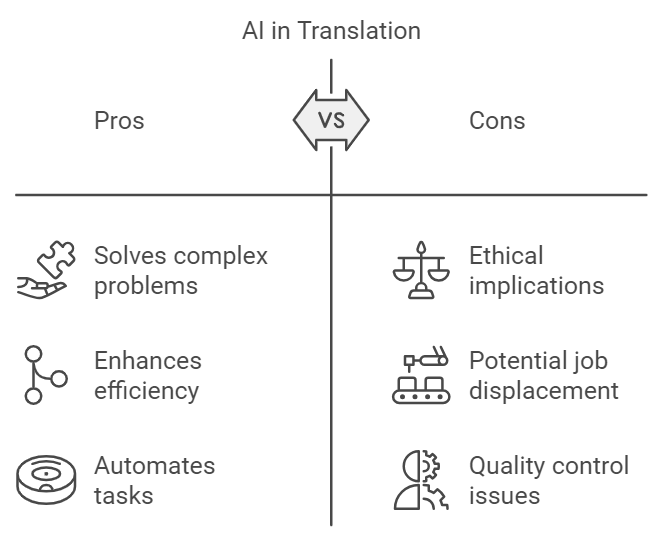
- Solving complex problems: AI can handle intricate translation tasks that would be daunting for humans alone.
- Enhancing business efficiency: Automated processes streamline operations, saving time and resources.
- Automating processes: AI takes over repetitive tasks, freeing up human experts for more nuanced work.
However, with great power comes great responsibility. As AI continues to improve translation quality and speed, we must address the ethical implications that come with this technology.
The Role of Human Expertise
While AI-driven translation tools are impressive, they are not infallible. Deep learning and natural language processing allow these tools to understand context and cultural nuances, but human expertise remains crucial for ensuring quality and handling complex or sensitive content.
Platforms Combining AI and Human Expertise
- Rapid Translate: Offers professional translation services that emphasize accuracy and customer support while incorporating AI tools to enhance efficiency.
- Globalization Partners International (GPI): Provides comprehensive software localization services, utilizing AI to manage multilingual projects and ensure consistency.
The symbiotic relationship between AI and human translators ensures that we get the best of both worlds – speed and accuracy. But there’s more to consider.
Generative AI and Its Challenges
Generative AI models like GPT-4 have shown promise in generating human-like text and performing translation tasks. However, these models are not yet as cost-effective or high-quality as specialized NMT engines. Companies like Lionbridge and AWS are integrating AI tools into their workflows to enhance productivity and reduce costs while maintaining human oversight for quality assurance.
Generative AI vs. Specialized NMT Engines
| Feature | Generative AI (e.g., GPT-4) | Specialized NMT Engines |
|---|---|---|
| Cost-effectiveness | Moderate | High |
| Translation Quality | Variable | Consistently High |
| Speed | Fast | Very Fast |
| Human Oversight Needed | Yes | Yes |
As we see, while generative AI holds potential, specialized NMT engines currently offer more reliable and cost-effective solutions for translation tasks.
The Importance of Data Annotation
Training AI models requires high-quality labeled data. This is where data annotation comes into play. Accurate machine learning outcomes depend on well-annotated data, and tools like Smartcat and services from companies like Shaip enable efficient data annotation and management.
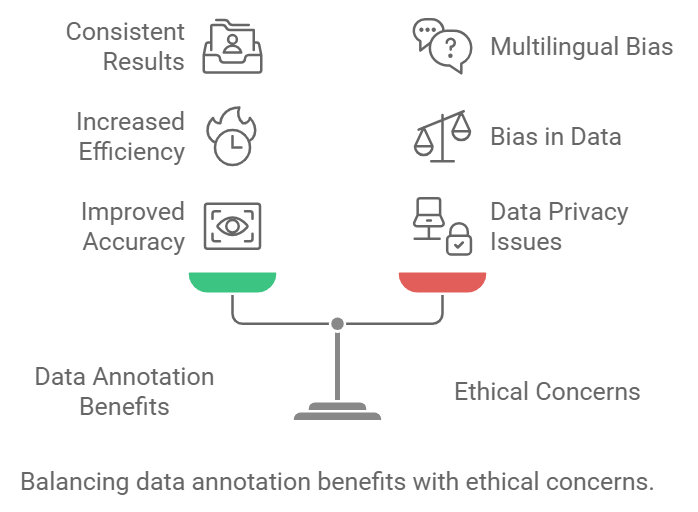
Benefits of High-Quality Data Annotation
- Improved Accuracy: Well-labeled data leads to more precise AI models.
- Efficiency: Streamlined data management supports faster AI adoption across industries.
- Consistency: Ensures uniformity in multilingual projects.
But we can’t talk about data without addressing the ethical concerns surrounding data privacy and bias.
Ethical Considerations in AI Translation
As we integrate AI more deeply into our lives, ethical considerations become paramount. Organizations like the CDC and the Pew Research Center emphasize the importance of transparent data practices and protecting user information.
Key Ethical Concerns
- Data Privacy: Ensuring that user data is collected, stored, and used responsibly.
- Bias Mitigation: Addressing and minimizing biases in AI models to ensure fair and accurate translations.
- Transparency: Being open about how AI models are trained and how data is used.
Practical Steps for Ethical AI Translation
- Implement robust data protection measures.
- Regularly audit AI models for biases.
- Maintain transparency with users about data practices.
By adhering to these ethical guidelines, we can harness the power of AI for translation while safeguarding user rights and promoting fairness.
AI in Various Industries
AI’s impact extends beyond translation. In healthcare, AI-driven solutions like Amazon HealthLake and Labby’s milk testing technology demonstrate the potential to improve data analysis and quality control. Similarly, AI applications in inventory management, as discussed by Madis Kuuse, showcase efficiency gains in logistics and supply chain optimization.
AI Applications in Different Sectors
- Healthcare: Enhanced data analysis and quality control.
- Logistics: Improved inventory management and supply chain optimization.
- Translation: Real-time multilingual communication and efficiency.
Latest Words
AI is undeniably transforming industries, making global communication more accessible and efficient. By integrating AI with human expertise, we ensure high-quality outcomes. However, it’s crucial to address the ethical considerations that come with this technology. As we move forward, let’s embrace AI’s potential while safeguarding our values and principles.
Quiz Time!
Before you go, let’s have a little fun. Answer this quiz in the comments below:
- What are the two main AI-driven translation technologies mentioned in the article?
- Why is human expertise still crucial in AI translation?
- Name one platform that combines AI tools with professional translation services.
- What are the three key ethical concerns in AI translation?
- How can we mitigate biases in AI models?
Looking forward to seeing your answers!
